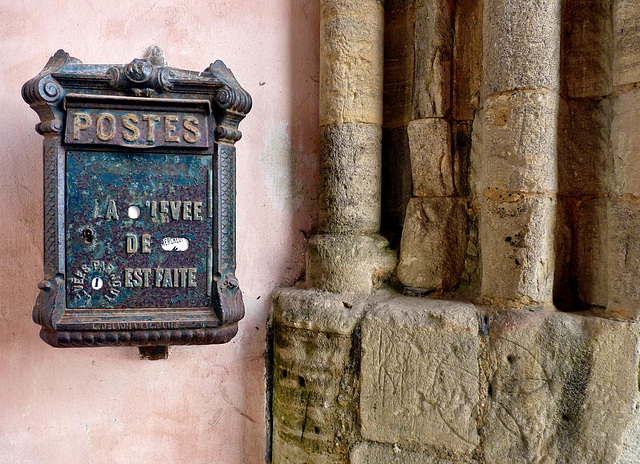Poste e Telegrafi
Venezia - Poste
Venice (ital. Venezia) is one of the most important tourist destinations worldwide with about 30 million visitors each year.
I have already uploaded dozens of shots from previous visits, so I´ll try to cut down the number of uploads this time.
Poste
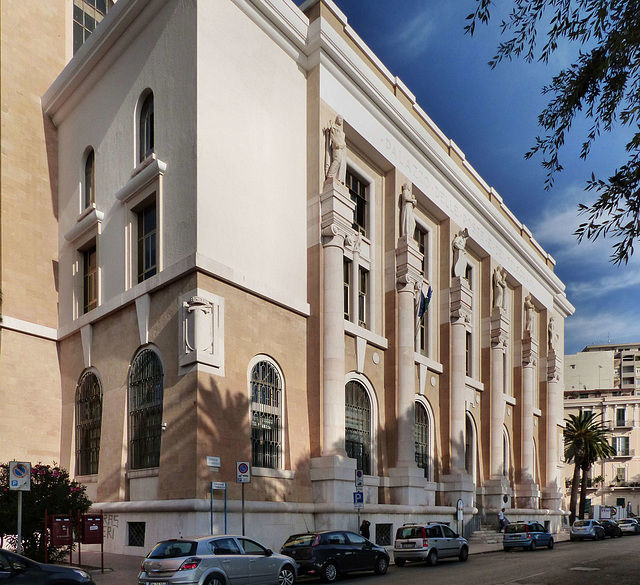
Taranto - Palazzo delle Poste
Taranto located on a peninsula was founded by Greek settlers and during the period of Greek colonization in Southern Italy, the city was among the most important in "Magna Graecia". During the Second Punic War, Taranto supported Hannibal in Italy and opened it´s doors to his troops in 212 BC, but when Romans recaptured Taranto three years later, they massacred the citizens and looted the town. It became a Roman colony later.
After the fall of the Roman Empire, Taranto got strongly fortified. In 547 Taranto asked a Byzantine general for support. He greatly reduced the size of the city in order to be able to defend it at all. So he separated the part of the isthmus from the actual city area, making an iland out of the peninsula and fortified it strongly. Nevertheless, three years later, the city was conquered by the Ostrogoth troops of Totila. Later Taranto was ruled by Langobards. The city was conquered by the Saracens in 839 and an emirate existed up to 880 when it was taken by a Byzantine army, but in 927 the Saracens were back looted and destroyed the city. It was rebuilt under Byzantine power from 967 on. The Normans conquered Taranto in the second half of the 11th century and founded the "Principality of Taranto" 1086. At that time the city was still strongly Greek and had a thriving Jewish community. Frederic II bequeathed the principality to his son Manfred.
The Taranto Post Office was built in 1935 - 1937. The building is 23 m high but only has four floors. It has the typical monumentality of the architecture of the fascist period.
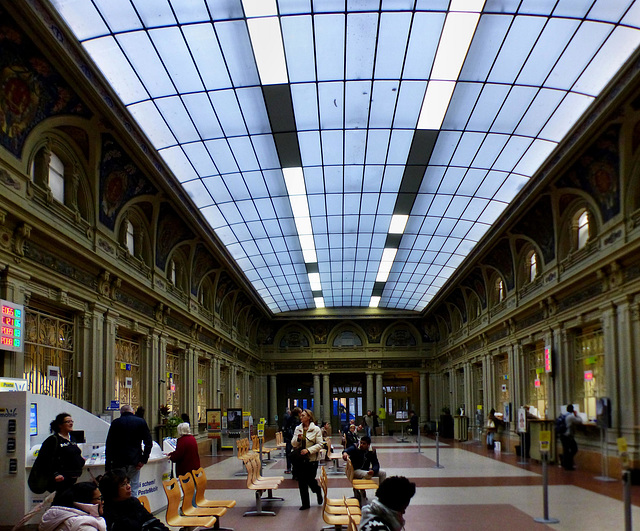
Parma - Ufficio Postale
The "Poste italiane" has this wonderful office in the center of Parma. Stamps for old fashioned postcards are sold here only on certain hours before noon. I did not believe this, but the person behind the counter made that very clear in the late afternoon.
Cerisy-la-Forêt - Abbey Saint-Vigor
Legends tell, that Saint Vigor, Bishop of Bayeux, founded a convent here within the 6th century.
In 1032 Robert I, Duke of Normandy, (aka "Robert the Magnificent", "Robert le Magnifique"), father of William the Conqueror, who became a pious man in his older age (and died during a pilgrimage to Jerusalem),
sponsored the Benedictine abbey and so the erection of the abbey-church started the same year.
The abbey was wealthy and important in medieval times, but declined like most other convents. It existed upto the French Revolution, when the last six monks were forced to leave. The abbey got sold and most of the conventual buildings got demolished.
The church was in a bad state after an earthquake (!) in 1775. It got renovated within the 19th century, since then serves the parish.
Like the church, the former gate house survived the times. The walls of the building are covered with carved graffiti and many decades ago "La Poste" installed a "Boîte aux lettres" here.
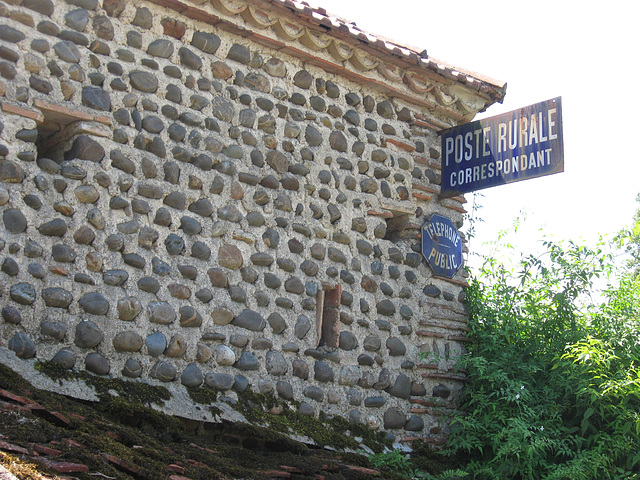
France - tres rural!
...the "Poste Rurale" was obviously closed and the "Public Telephone" as well...
Coimbra - Post Office
A Roman settlement, named "Aeminium" existed here. When the neighbouring town "Conimbriga" got conquered and destroyed by the Suebes in 468, the survivors moved to "Aeminium" - and renamed it. The Visigoths under King Wittiza named the town "Eminio" later. In 714 the town was conquered by Muslim troops, who changed the name again.
Coimbra was finally recaptured in 1064 by King Fernando de Castilla y León. Coimbra became the second capital of the Kingdom of Portugal (after Guimarãesin) 1139, a status that moved to Lisbon in 1256. The University of Coimbra, founded by Denis of Portugal (aka "Dom Dinis") in 1290, is one of the oldest in Europe.
When telephony and telegraphy changed the world, architects designed post offices sometimes as modern "temples of hitech".
Berlin - Postfuhramt
Berlin is the capital and largest city of Germany. The city is one of Germany's 16 federal states.
The first records of towns in the area of present-day Berlin date from the late 12th century. The central part of Berlin can be traced back to two towns. Cölln on the Fischerinsel is first mentioned in 1237 and Berlin, across the river Spree in 1244. The two towns over time formed close economic and social ties, and profited from the staple right on the two important trade routes Via Imperii and from Bruges to Novgorod.
In 1415, Frederick I became the elector of the Margraviate of Brandenburg. His successors established Berlin-Cölln as capital of the margraviate, and subsequent members of the Hohenzollern family ruled in Berlin until 1918, first as electors of Brandenburg, then as kings of Prussia, and eventually as German emperors.
The Thirty Years' War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. The city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the "Grosse Kurfürst" initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance from 1640 on. In 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the Huguenots. By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlin's residents were French Huguenots. Other immigrants came from Bohemia and Poland.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the city's economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire.
In 1933 the Nazi Party came to power. After the "Kristallnacht" progrom in 1938, thousands of the city's Jews were imprisoned in the nearby Sachsenhausen concentration camp. Starting in 1943, many were shipped to death camps, such as Auschwitz.
During World War II, large parts of Berlin were destroyed by Allied air raids and the 1945 Battle of Berlin. Around 125,000 civilians were killed. After the end of WWII , by Berlin received large numbers of refugees from the Eastern provinces. The victorious powers divided the city into four sectors, analogous to the occupation zones into which Germany was divided. The sectors of the Western Allies formed West Berlin, while the Soviet sector formed East Berlin.
The Berlin Wall was a barrier that divided the city from 1961 to 1989, when it fell. In October 1990, the German reunification process was formally finished.
-
Since 1766, here was the post office with living quarters of the royal postmaster, a general contractor, who took over all duties of the postal service.
Due to the growing post traffic in Berlin, a new structure was necessary in the second half of the 19th century. As the former structure could not offer a place for the more than 250 horses needed for the increasing transport business, the representative brick building on Oranienburger Straße was erected 1875 - 1881. At that time it was one of the largest public buildings in Berlin.
When the post office was fundamentally modernized in 1925, these stable buildings disappeared. The Postfuhramt suffered considerable damage during WWII. In 1944 it burned down to the first floor. In 1973, the first minor restoration work began. The courtyard facade of the wing on the Oranienburger Straße was restored greatly simplified. The restoration of the corner building part including the tower and domes was done 1986 - 1989.
Ferrara - Poste e Telegrafi
Ferrara appears first in a document of the Lombard king Desiderius of 753 when he captured the town from the Exarchate of Ravenna. Later the Franks, after routing the Lombards, presented Ferrara to the Papacy in 754. In 988 Ferrara was ceded by the Church to the House of Canossa, but at the death of Matilda of Tuscany in 1115, it became a free commune. During the 12th century, the history of the town was marked by the wrestling for power between the Guelph Adelardi and the Ghibelline Salinguerra families. The Ghibellines won and in 1264 Obizzo II d'Este was proclaimed lifelong ruler of Ferrara. His rule marked the end of the communal period in Ferrara and the beginning of the Este rule, which lasted until 1598.
Poste e Telegrafi
Moudon - Postes et Telegraphes
Moudon, today a town with a population of about 6000, was called Minnodunum. In Roman times. Moudon was under the influence of the Savoy already in the early 13th century and became an important Savoyard base in Waadt / Vaud. Around 1260, under Peter of Savoy, it became the residence of the Savoy bailiff in Vaud. The importance of Moudon increased rapidly. The town area expanded and was surrounded by new walls. In 1285, Moudon was granted town privileges. Especially in the 14th and 15th centuries, the town flourished as an administrative center and of the Vaudois estates. With the conquest of Vaud by Bern in 1536, Moudon came under Bernese rule. The Reformation was introduced.
Communication became very important with industrialization. Post offices were often "temples" of the new technology.
Jump to top
RSS feed- Latest items - Subscribe to the latest items added to this album
- ipernity © 2007-2025
- Help & Contact
|
Club news
|
About ipernity
|
History |
ipernity Club & Prices |
Guide of good conduct
Donate | Group guidelines | Privacy policy | Terms of use | Statutes | In memoria -
Facebook
Twitter